|
Summary:
|
|
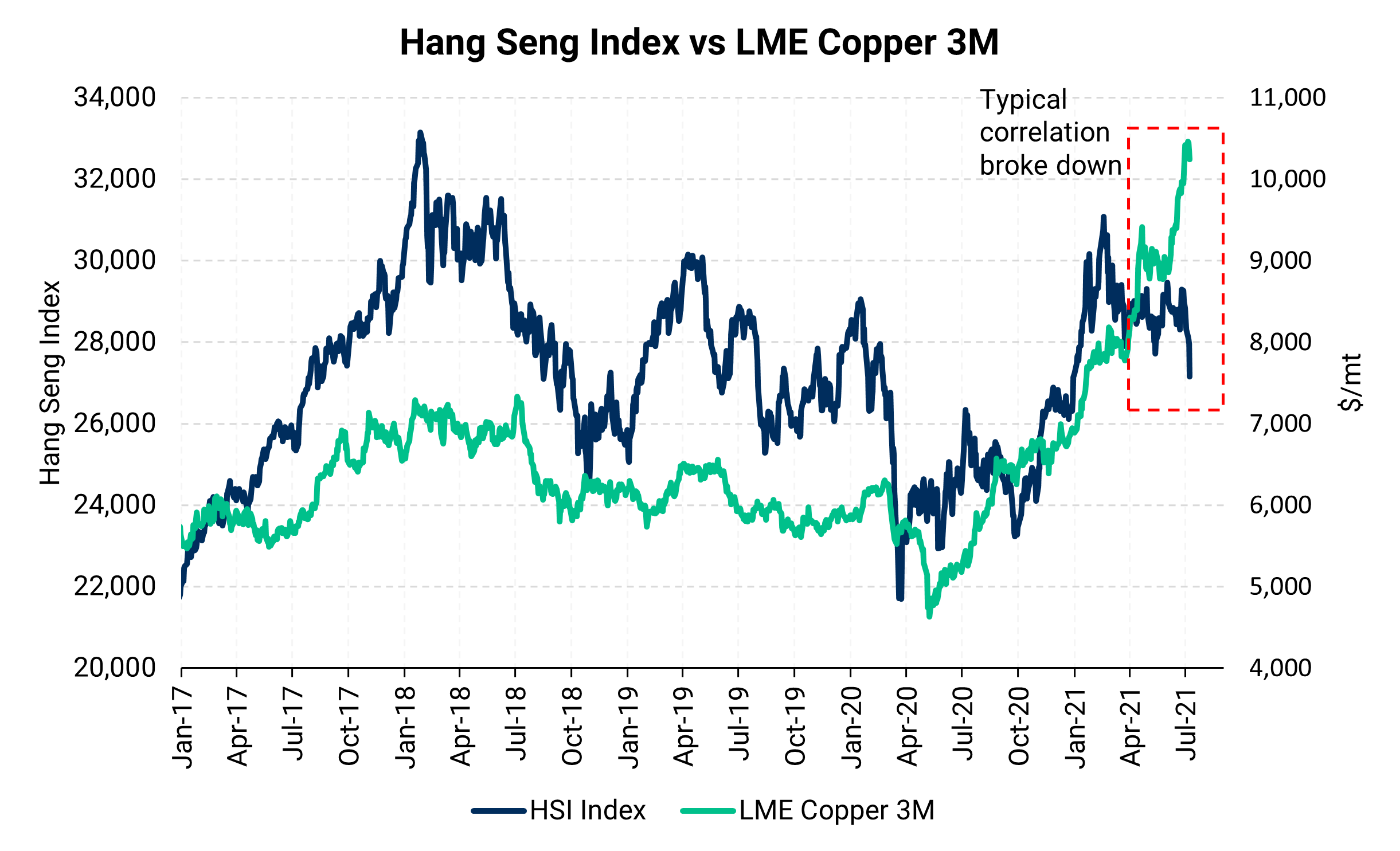
AEGIS Thoughts & Strategies: In an effort to cool inflation, China has recently open its metals reserves, as the first auctions occured last Monday and Tuesday (July 5-6). To restimulate the economy, China’s cabinet announced on Wednesday (July 7) that it will implement a variety of monetary tools, including lowering the banking reserve requirement ratio (RRR). Wednesday's statements were followed on Friday by the announcement that they will lower the RRR by 50 basis points, effective July 15. To clarify, the RRR is portion of reserves that banks must keep “in the vault." By lowering this requirement, banks can do more lending and better support the larger economy. The government is also requesting that banks lower financing costs to smaller companies. However, their stimulus efforts have the potential of creating inflation, as lowering financing costs for borrowers and other monetary stimuli incentivizes producers to obtain lower interest rate loans to rebuild inventories of raw materials. This could potentially drive prices of raw materials and finished goods ever higher. So which effort will win out? For now, the bulls have the upperhand; however, slower economic growth from China is likely to limit copper demand, and sales of China's reserve metals puts pressure on prices. These would balance against the country's efforts to incentivize investment. |